Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Be and
Be and  Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxes
Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxesSakurai, Hirohisa*; Kurebayashi, Yutaka*; Suzuki, Soichiro*; Horiuchi, Kazuho*; Takahashi, Yui*; Doshita, Norihiro*; Kikuchi, Satoshi*; Tokanai, Fuyuki*; Iwata, Naoyoshi*; Tajima, Yasushi*; et al.
Physical Review D, 109(10), p.102005_1 - 102005_18, 2024/05
Secular variations of galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) are inseparably associated with the galactic activities and should reflect the environments of the local galactic magnetic field, interstellar clouds, and nearby supernova remnants. The high-energy muons produced in the atmosphere by high-energy GCRs can penetrate deep underground and generate radioisotopes in the rock. As long lived radionuclides such as  Be and
Be and  Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of
Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of  Be and
Be and  Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced
Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced  Be and
Be and  Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
Kido, Eiji*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Kobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Nagataki, Shigehiro*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Tamii, Atsushi*; Utsuno, Yutaka
Astroparticle Physics, 152, p.102866_1 - 102866_12, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:50.35(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Amenomori, Michihiro*; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Tibet AS Collaboration*; 116 of others*
Collaboration*; 116 of others*
Astrophysical Journal, 954(2), p.200_1 - 200_7, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:44.78(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Amenomori, Michihiro*; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Tibet AS Collaboration*; 111 of others*
Collaboration*; 111 of others*
Physical Review Letters, 127(3), p.031102_1 - 031102_6, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:86.79(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Amenomori, Michihiro*; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Tibet AS Collaboration*; 93 of others*
Collaboration*; 93 of others*
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(5), p.460 - 464, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:98.88(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Amenomori, Michihiro*; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Tibet AS Collaboration*; 93 of others*
Collaboration*; 93 of others*
Physical Review Letters, 126(14), p.141101_1 - 141101_7, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:119 Percentile:99.56(Physics, Multidisciplinary)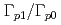 ratios of resonance states in
ratios of resonance states in  Be for deducing the
Be for deducing the  Be(
Be( ,
,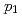 )
) Li
Li reaction rate relevant to the cosmological lithium problem
reaction rate relevant to the cosmological lithium problemIwasa, Naohito*; Ishikawa, Shunki*; Kubono, Shigeru*; Sakakibara, T.*; Kominato, Kazuya*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Matsuda, Makoto; Hirose, Kentaro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Orlandi, R.; et al.
Physical Review C, 103(1), p.015801_1 - 015801_5, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:18.12(Physics, Nuclear)Omori, Yasutaka*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Sanada, Tetsuya*; Hirao, Shigekazu*; Ono, Koji*; Furukawa, Masahide*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 40(3), p.R99 - R140, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:75.48(Environmental Sciences)UNSCEAR and the Nuclear Safety Research Association report the annual effective doses from cosmic rays, terrestrial radiation, inhalation and ingestion from natural sources. In this study, radiation doses from natural radiation sources in Japan were reviewed with the latest knowledge and data. Total annual effective dose from cosmic-ray exposure can be evaluated as 0.29 mSv. The annual effective dose from external exposure to terrestrial radiation for Japanese population can be evaluated as 0.33 mSv using the data of nationwide survey by the National Institute of Radiological Sciences. The Japan Chemical Analysis Center (JCAC) performed the nationwide radon survey using a unified method for radon measurements in indoor, outdoor and workplace. The annual effective dose for radon inhalation was estimated using a current dose conversion factor, and the values were estimated to be 0.50 mSv. The annual effective dose from thoron was reported as 0.09 mSv by UNSCEAR and then the annual effective dose from inhalation can be described as 0.59 mSv. According to the report of large scale survey of foodstuff by JCAC, the effective dose from main radionuclides due to dietary intake can be evaluated to be 0.99 mSv. Finally, Japanese population dose from natural radiation can be assessed as 2.2 mSv which is near to the world average value of 2.4 mSv.
Amenomori, Michihiro*; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Tibet AS Collaboration*; 89 of others*
Collaboration*; 89 of others*
Physical Review Letters, 123(5), p.051101_1 - 051101_6, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:125 Percentile:98.49(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Miyazawa, Yu*; Ikegami, Masashi*; Miyasaka, Tsutomu*; Oshima, Takeshi; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Hirose, Kazuyuki*
Proceedings of 42nd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC-42) (CD-ROM), p.1178 - 1181, 2015/06
Abderrahmane, A.*; Ko, P. J.*; Okada, Hiroshi*; Sato, Shinichiro; Oshima, Takeshi; Shibasaki, Ichiro*; Sandhu, A.*
IEEE Electron Device Letters, 35(12), p.1305 - 1307, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.41(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Tolerance of AlInSb/InAsSb/AlInSb heterostructures quantum-well-based micro-Hall sensors against proton irradiation of 380 keV and proton fluence in the range 10 and 10
and 10 (proton/cm
(proton/cm ) is reported. Defects and deep levels induced by proton irradiation into the heterostructures caused decreases in the mobility of the micro-Hall sensors. Degradation of the magnetic sensitivity started at a proton fluence of 10
) is reported. Defects and deep levels induced by proton irradiation into the heterostructures caused decreases in the mobility of the micro-Hall sensors. Degradation of the magnetic sensitivity started at a proton fluence of 10 (proton/cm
(proton/cm ) and continued with increasing proton fluence. The variation of the micro-Hall sensors sensitivity was minimal in low doped AlInSb/InAsSb/AlInSb heterostructure quantum wells. These micro-Hall sensors were operable even at proton fluence of 10
) and continued with increasing proton fluence. The variation of the micro-Hall sensors sensitivity was minimal in low doped AlInSb/InAsSb/AlInSb heterostructure quantum wells. These micro-Hall sensors were operable even at proton fluence of 10 (proton/cm
(proton/cm ), which makes these devices suitable for space applications with lifetime of thousands of years in the outer space.
), which makes these devices suitable for space applications with lifetime of thousands of years in the outer space.
Hubbard, S.*; Sato, Shinichiro; Schmieder, K.*; Strong, W.*; Forbes, D.*; Bailey, C. G.*; Hoheisel, R.*; Walters, R. J.*
Proceedings of 40th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC-40) (CD-ROM), p.1045 - 1050, 2014/06
Baseline and quantum dot (QD) GaAs pn-junction diodes were characterized by deep level transient spectroscopy before and after both 1MeV electron irradiation and 140 keV proton irradiation. Prior to irradiation, the addition of quantum dots appeared to have introduced a higher density of defects at EC-0.75 eV. After 1 MeV electron irradiation the well-known electron defects E3, E4 and E5 were observed in the baseline sample. In the quantum dot sample after 1 MeV electron irradiation, defects near E3, E4 and EC-0.75 eV were also observed. Compared to the irradiated baseline, the QD sample shows a higher density of more complex E4 defect and a lower density of the simple E3 defect, while the EC-0.75 eV defect seemed to be unaffected by electron irradiation. As well, after proton irradiation, well known proton defects PR1, PR2, PR4' are observed. The QD sample shows a lower density PR4' defects and a similar density of PR2 defects, when compared to the proton irradiated baseline sample.
Maximenko, S.*; Lumb, M.*; Hoheisel, R.*; Gonz lez, M.*; Scheiman, D.*; Messenger, S.*; Tibbits, T. N. D.*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Oshima, Takeshi; Sato, Shinichiro; et al.
lez, M.*; Scheiman, D.*; Messenger, S.*; Tibbits, T. N. D.*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Oshima, Takeshi; Sato, Shinichiro; et al.
Proceedings of 40th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC-40) (CD-ROM), p.2144 - 2148, 2014/06
In this paper, a complex analysis of the radiation response of GaAs solar cells with multi quantum wells (MQW) incorporated in the i-region of the device is presented. Electronic transport properties of the MQW i-region were assessed experimentally by the electron beam induced current (EBIC) technique. A 2-D EBIC diffusion model was applied to simulate EBIC line scans across device structure for different radiation doses. The results are interpreted using numerical modeling of the electrical field distribution at different radiation levels. Type conversion from n- to p-type was found in MQW i-region at displacement damage dose as low as low as 1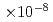 MeV MeV/g. This is supported by experimental and simulated EBIC and electric field distribution results.
MeV MeV/g. This is supported by experimental and simulated EBIC and electric field distribution results.
Shimazaki, Kazunori*; Kobayashi, Yuki*; Takahashi, Masato*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Murashima, Mio*; Takahashi, Yu*; Toyota, Hiroyuki*; Kukita, Akio*; Oshima, Takeshi; Sato, Shinichiro; et al.
Proceedings of 40th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC-40) (CD-ROM), p.2149 - 2154, 2014/06
The electrical performance of a glass-type space solar sheet (G-SSS) was demonstrated in space. G-SSS comprises InGaP/GaAs dual-junction and InGaP/GaAs/InGaAs triplejunction solar cells. It is lightweight solar generation sheet, less than 0.5 mm thick. It is mounted on the "HISAKI" (SPRINT-A) small scientific satellite, which was launched on September 14, 2013. The initial flight data were successfully acquired and this flight demonstration was a world-first experiment for G-SSS using III-V multi-junction thin-film solar cells. The cells demonstrated superior performance and the electrical outputs matched the flight prediction.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Sihver, L.*
Radiation Measurements, 41(9-10), p.1142 - 1146, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:87.51(Nuclear Science & Technology)The applicability of PHITS to the shielding design of spacecrafts was examined by comparing calculated neutron spectra and doses for astronauts in the Space Shuttle with the corresponding experimental data. The agreements between the data were quite satisfactory, especially for the neutron spectra, which have been barely reproduced by other studies. We therefore concluded that PHITS has a great possibility of playing an important role in the design study of spacecrafts.
Arakawa, Kazuo
Hoshasen Kagaku, (80), p.57 - 59, 2005/09
no abstracts in English
 W,
W,  Re and
Re and  Os; Implications for the Re-Os cosmochronology
Os; Implications for the Re-Os cosmochronologyShizuma, Toshiyuki; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Mohr, P.*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Goko, Shinji*; Makinaga, Ayano*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Ota, Masahisa*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 72(2), p.025808_1 - 025808_9, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:90.03(Physics, Nuclear)Cross sections of the  W,
W,  Re,
Re,  Os(
Os(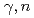 ) reactions were measured using quasi-monochromatic photon beams from laser Compton scattering (LCS) with average energies from 7.3 to 10.9 MeV. The results are compared with the predictions of Hauser-Feshbach statistical calculations using four different sets of input parameters. In addition, the inverse neutron capture cross sections were evaluated by constraining the model parameters, especially the
) reactions were measured using quasi-monochromatic photon beams from laser Compton scattering (LCS) with average energies from 7.3 to 10.9 MeV. The results are compared with the predictions of Hauser-Feshbach statistical calculations using four different sets of input parameters. In addition, the inverse neutron capture cross sections were evaluated by constraining the model parameters, especially the  strength function, on the basis of the experimental data. The present experiment helps to further constrain the correction factor
strength function, on the basis of the experimental data. The present experiment helps to further constrain the correction factor 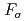 for the neutron capture on the 9.75 keV state in
for the neutron capture on the 9.75 keV state in  Os. Implications of
Os. Implications of 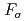 to the Re-Os cosmochronology are discussed with a focus on the uncertainty in the estimate of the age of the Galaxy.
to the Re-Os cosmochronology are discussed with a focus on the uncertainty in the estimate of the age of the Galaxy.
 -process path and its implications for a
-process path and its implications for a  Re-
Re- Os nucleo-cosmochronometer
Os nucleo-cosmochronometerHayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Kajino, Toshitaka*; Chiba, Satoshi; Shinohara, Nobuo; Nakagawa, Tsuneo; Arima, Taiko*
Astrophysical Journal, 628(1, Part1), p.533 - 540, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:51.44(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
 -process and the
-process and the  Lu nuclear cosmochronometer
Lu nuclear cosmochronometerHayakawa, Takehito; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Kajino, Toshitaka*; Umeda, Hideyuki*; Nomoto, Kenichi*
Nuclear Physics A, 758, p.525c - 528c, 2005/07
no abstracts in English